Encountering a snake in the wild can be a nerve-wracking experience, especially if you’re bitten. While most snakebites are not life-threatening, knowing how to administer first aid can make a significant difference in the outcome.
In this blog post, we’ll explore the effects of snakebites, common symptoms, and the appropriate first aid measures to take in case of a snakebite emergency.
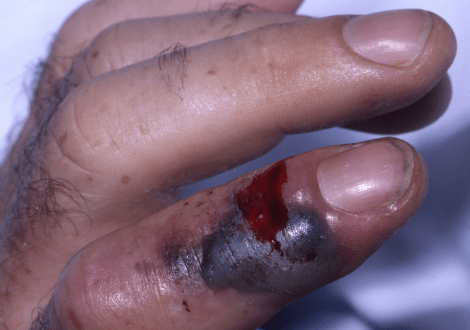
Understanding the Effects of Snakebites:
When a snake injects venom into its victim through a bite, the effects can vary depending on the species of snake, the amount of venom injected, and the individual’s reaction.
Venomous snakes inject venom primarily to immobilize prey or defend themselves from perceived threats. The venom can cause a range of symptoms, from mild to severe, including:
- Local effects: Immediate pain, swelling, redness, and bruising at the site of the bite are common local effects of snake venom.
- Systemic effects: Venom can also cause systemic effects throughout the body, including nausea, vomiting, dizziness, weakness, difficulty breathing, and changes in heart rate and blood pressure.
- Neurotoxic effects: Some snake venoms contain neurotoxins that can affect the nervous system, leading to symptoms such as paralysis, blurred vision, slurred speech, and difficulty swallowing.
- Hemotoxic effects: Other snake venoms contain hemotoxins that can disrupt blood clotting and cause internal bleeding, tissue damage, and organ failure.
Common Symptoms of Snakebites: Recognizing the symptoms of a snakebite is crucial for providing timely first aid and seeking appropriate medical treatment. Common symptoms may include:
- Immediate pain or burning sensation at the site of the bite
- Swelling, redness, and bruising around the bite area
- Nausea, vomiting, and dizziness
- Weakness, fatigue, and fainting
- Difficulty breathing or swallowing
- Blurred vision or drooping eyelids
- Paralysis or numbness in the affected limb
First Aid for Snakebite: If you or someone you’re with is bitten by a snake, it’s essential to take immediate action while waiting for medical help to arrive. Here are the steps to follow for providing first aid:
- Stay calm: Keep the victim calm and reassure them while you assess the situation and administer first aid.
- Keep the affected limb immobilized: Encourage the victim to remain still and avoid moving the bitten limb to prevent the spread of venom through the bloodstream.
- Remove tight clothing or jewelry: Remove any tight clothing or jewelry from the affected area, as swelling may occur.
- Clean the wound: Gently clean the bite wound with soap and water to reduce the risk of infection, but avoid applying ice or tourniquets, as these can worsen tissue damage.
- Apply a pressure bandage: If possible, apply a pressure bandage above the bite site to help slow the spread of venom. Ensure that the bandage is firm but not too tight, and leave the fangs visible to help identify the snake species.
- Seek medical help: Call emergency services or transport the victim to the nearest hospital as soon as possible for further evaluation and treatment by healthcare professionals.
Conclusion:
Snakebites can be a frightening and potentially life-threatening experience, but knowing how to administer first aid can greatly improve the chances of a positive outcome.
By understanding the effects of snakebites, recognizing common symptoms, and taking prompt action to provide first aid, you can help minimize the severity of the injury and ensure that the victim receives the appropriate medical treatment.
Remember, when it comes to snakebites, quick and effective first aid can make all the difference in saving lives.
